Skillnad mellan versioner av "3.3 Ekvationer+"
Taifun (Diskussion | bidrag) m |
Taifun (Diskussion | bidrag) m |
||
| Rad 89: | Rad 89: | ||
| − | :<big><b> | + | :<big><b>[[3.3_Ekvationer#Ekvationsl.C3.B6sning:_Allm.C3.A4n_metod|Mer info >> ]]</b></big> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Versionen från 10 december 2016 kl. 12.56
| Genomgång Ekvationer | Genomgång Potensekvationer | Quiz | Övningar | Lathund |
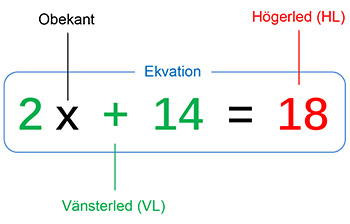
Vad är en ekvation?
En ekvation är en likhet mellan två uttryck
som innehåller endast EN variabel, kallad
obekant, se exemplet ovan.
En ekvation har alltid formen VL = HL .
Ekvationens lösning: \( \quad\; \)Kontroll: Sätt in lösningen i ekvationen.
VL \( \, = \, 2 \, \cdot \, {\color{Red} 2} \, + \, 14 \, = \, 4 \, + \, 14 \, = \, 18 \)
HL \( \, = \, 18 \)
VL \( \; = \; \) HL \( \qquad \Longrightarrow \qquad \) OK
Dvs lösningen \( \, x = {\color{Red} 2} \, \) är korrekt.
Kontroll kallas ibland även för prövning.
Ekvationslösning: Övertäckningsmetoden
Exemplet ovan:
\( 2 \, x \;\; + \; 14 \; = \; 18 \quad {\color{Red} {\rm Täck\;över\;}} 2 \, x \)
\( \;\, {\color{Red} 4} \;\;\; + \; 14 \; = \; 18 \)
\( \;\, \Downarrow \)
\( \, 2 \, \cdot \; x \;\; = \;\, {\color{Red} 4} \qquad\quad {\color{Red} {\rm Täck\;över\;}} x \)
\( \, 2 \, \cdot \; \)\( \, 2 \, \cdot \; {\color{Red} 2} \;\; = \;\; 4 \)
\( \quad\;\;\; \Downarrow \)
Ekvationslösning: Allmän metod
Exemplet ovan:
- \[\begin{array}{rclcl} 2\,x \, + \, 14 & = & 18 & & \\ 2\,x \, + \, 14 \, {\color{Red} {- \, 14}} & = & 18 \, {\color{Red} {- \, 14}} & & \\ 2 \cdot x \, & = & 4 & & \\ \displaystyle \frac{2 \cdot x}{{\color{Red} {2}}} & = & \displaystyle \frac{4}{{\color{Red} {2}}} & & \\ x \, & = & 2 & & \end{array}\]
Ekvationer med obekanten \( \, x \, \) i båda leden
Potensekvationer
Copyright © 2010-2016 Math Online Sweden AB. All Rights Reserved.